Treatments
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine and metabolic disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by a combination of ovulatory dysfunction, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovarian morphology, though not all women present with every feature.
Epidemiology:
- Affects ~6–12% of women of reproductive age (varies by diagnostic criteria).
- Leading cause of anovulatory infertility.
Etiology & Pathophysiology:
- The exact cause is multifactorial: genetic, hormonal, and environmental.
- Key mechanisms:
- Insulin resistance & hyperinsulinemia → stimulates ovarian androgen production.
- Hyperandrogenism → hirsutism, acne, alopecia, anovulation.
- Disrupted HPO (hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian) axis → abnormal LH:FSH ratio, impaired follicular development.
Diagnostic Criteria:
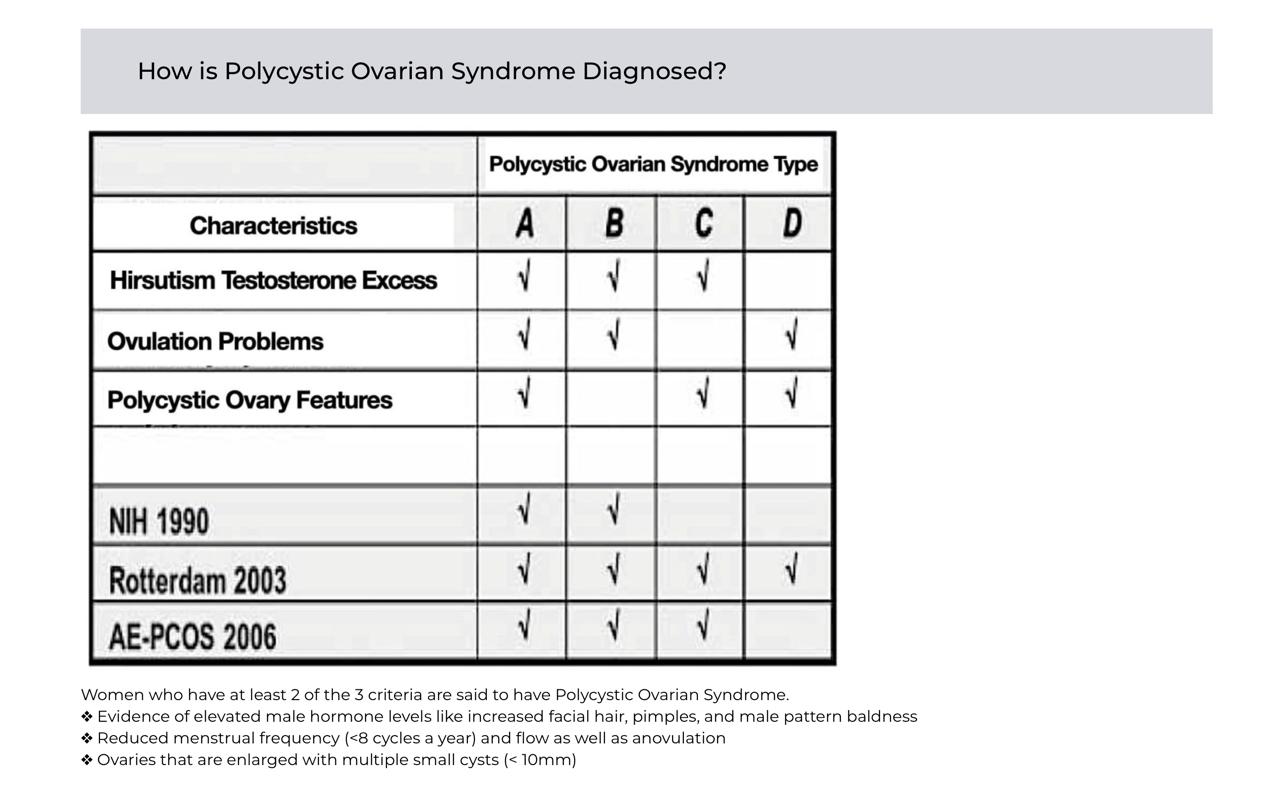
The most widely used is the Rotterdam Criteria (2003): at least 2 out of 3:
- Oligo-ovulation or anovulation (irregular or absent cycles).
- Clinical and/or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism (e.g., hirsutism, acne, elevated testosterone).
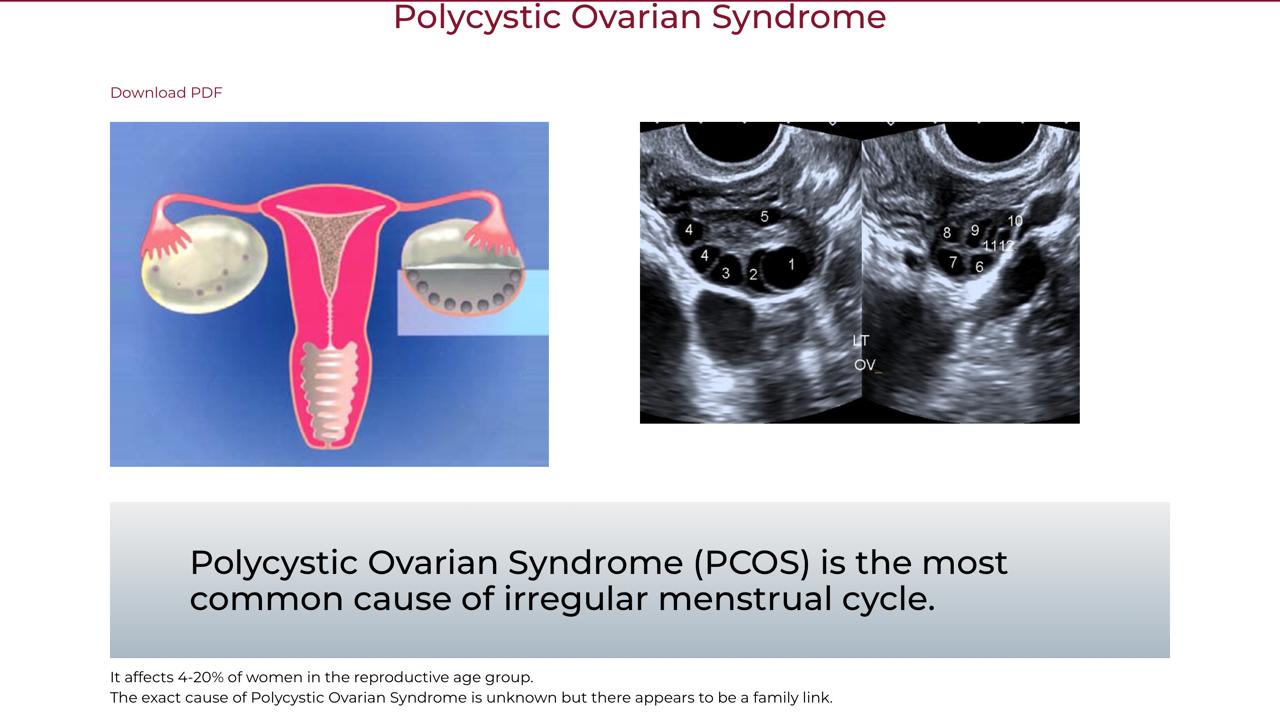
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound (≥12 follicles 2–9 mm or ovarian volume >10 mL).
(Other causes must be excluded, such as thyroid disorders, hyperprolactinemia, or congenital adrenal hyperplasia.)
Clinical Features:
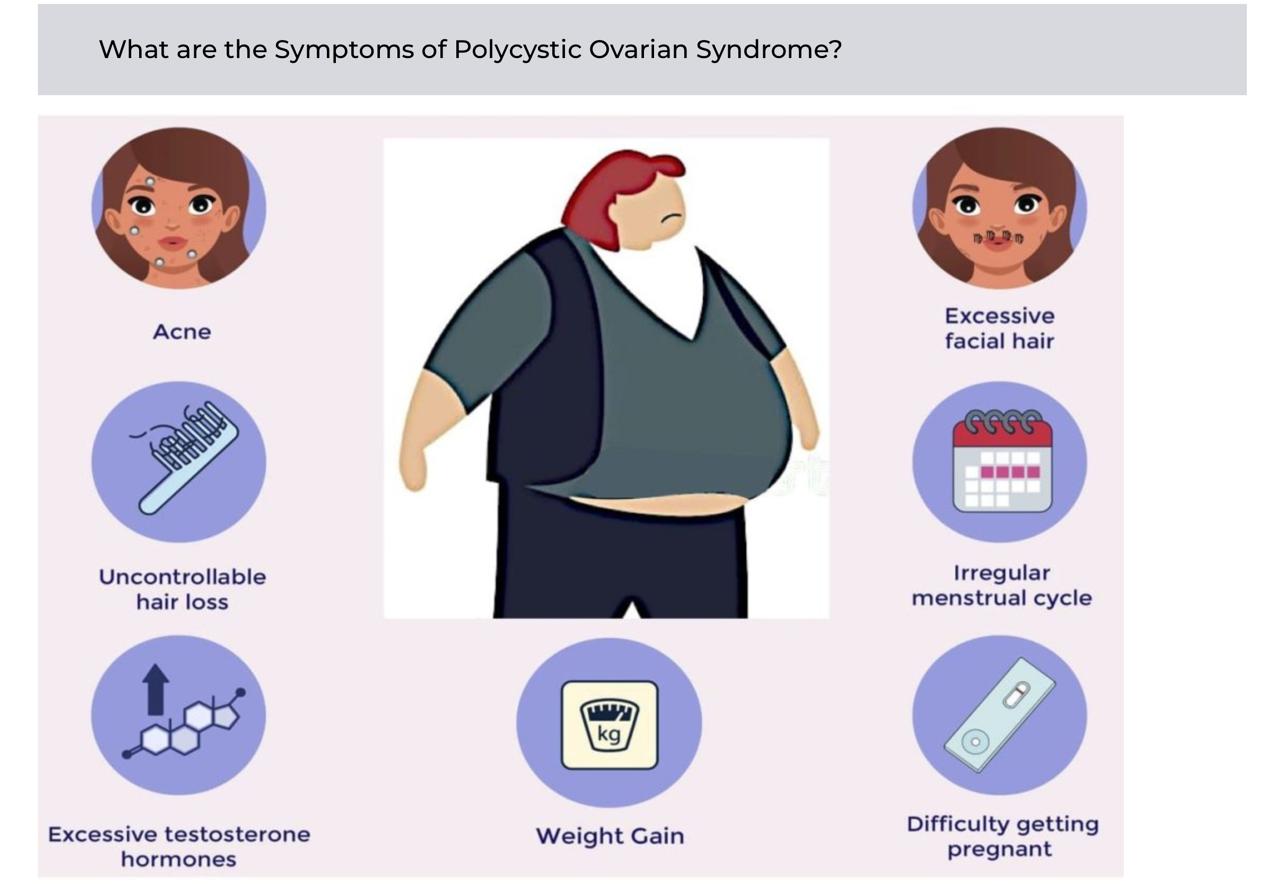
- Menstrual/ovulatory dysfunction: oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, infertility.
- Hyperandrogenism: hirsutism, acne, male-pattern hair loss.
- Metabolic manifestations: insulin resistance, obesity (especially central), increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Long-term risks: endometrial hyperplasia/cancer (due to chronic anovulation), dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease.
Investigations:
- Hormonal profile: ↑ androgens, ↑ LH:FSH ratio (sometimes), rule out mimicking conditions.
- Ultrasound pelvis: “string of pearls” appearance of multiple small follicles.
- Metabolic evaluation: fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile.
Management:
Treatment is individualized depending on patient’s symptoms and fertility goals.
- Lifestyle modification:
- Weight loss (5–10%) improves ovulation and insulin sensitivity.
- Regular exercise, balanced diet (low GI, high fiber).
- Pharmacological management:
- Menstrual irregularity / hyperandrogenism:
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) regulate cycles, reduce hirsutism/acne.
- Anti-androgens (spironolactone, finasteride) if needed.
- Insulin resistance:
- Metformin improves metabolic profile and may restore ovulation.
- Infertility:
- Ovulation induction agents (letrozole, clomiphene citrate).
- Assisted reproductive techniques if resistant.
- Cosmetic measures for hirsutism:
- Laser hair removal, electrolysis, topical eflornithine.